Abstract
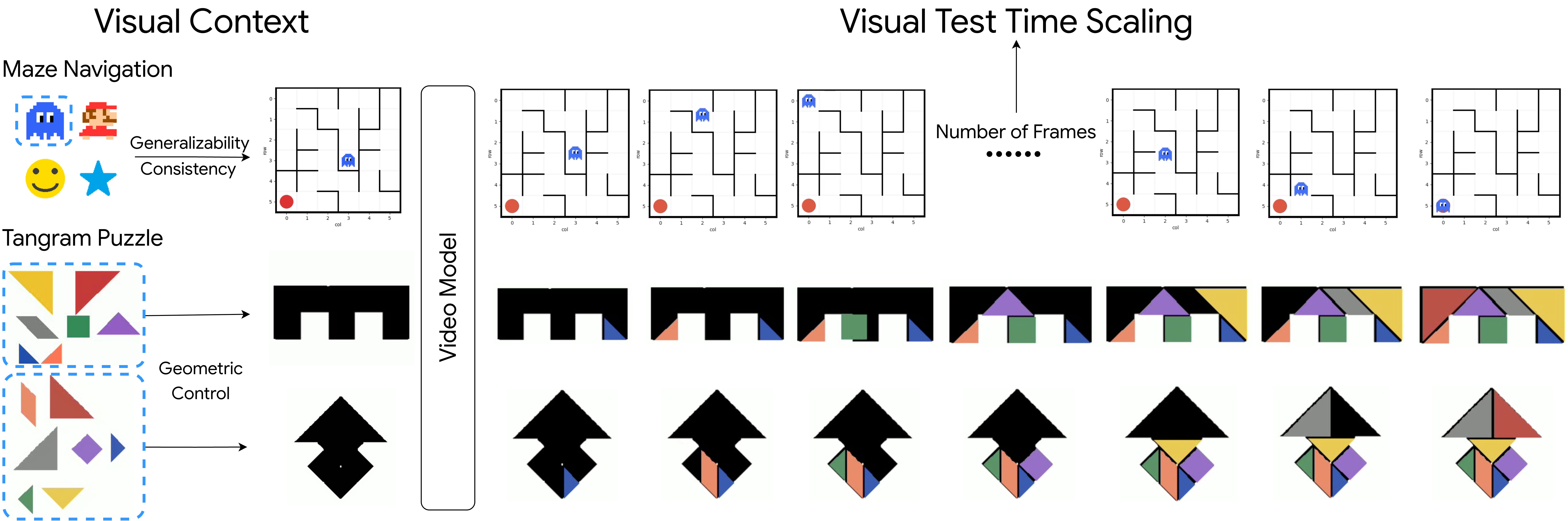
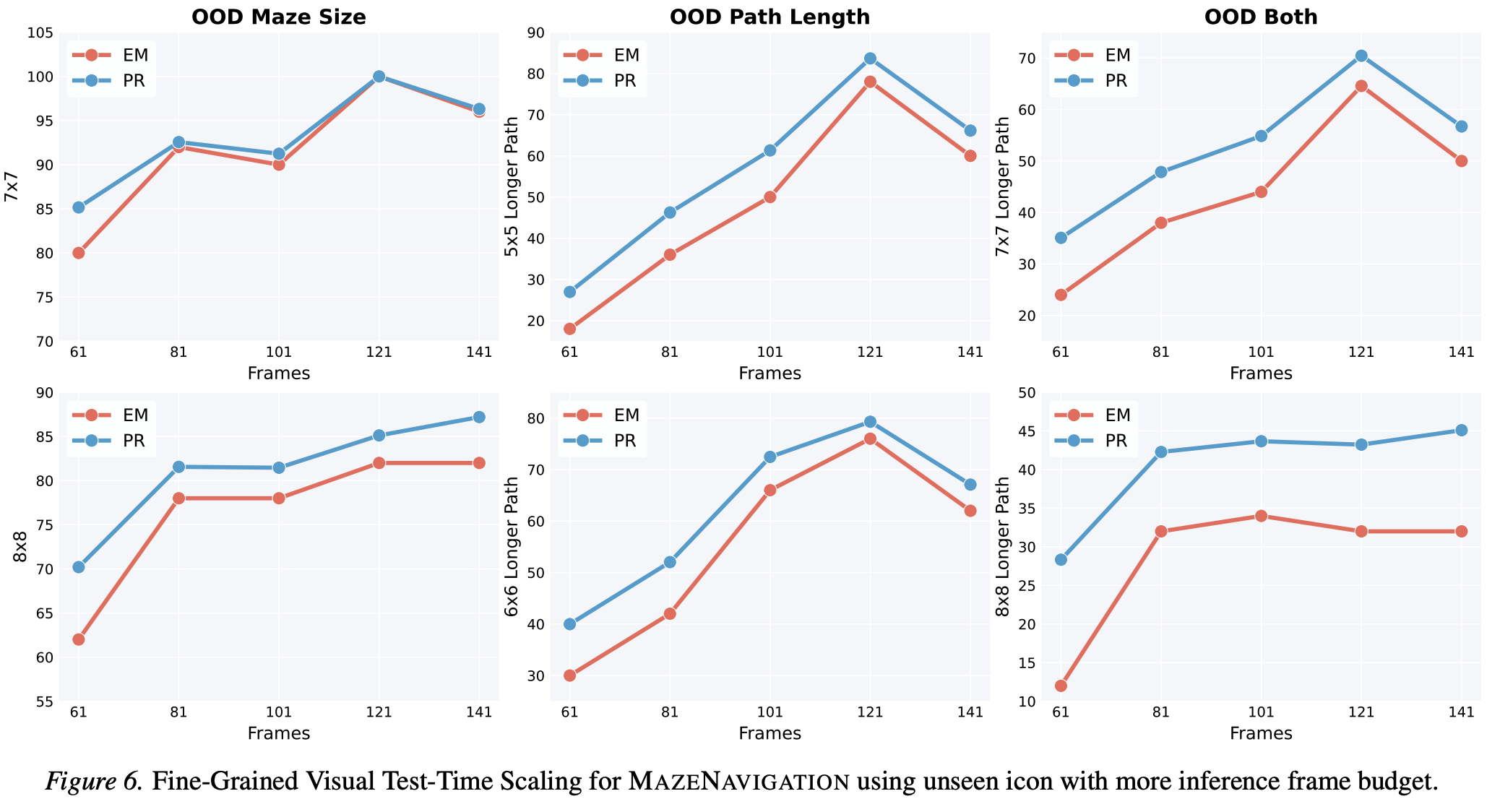
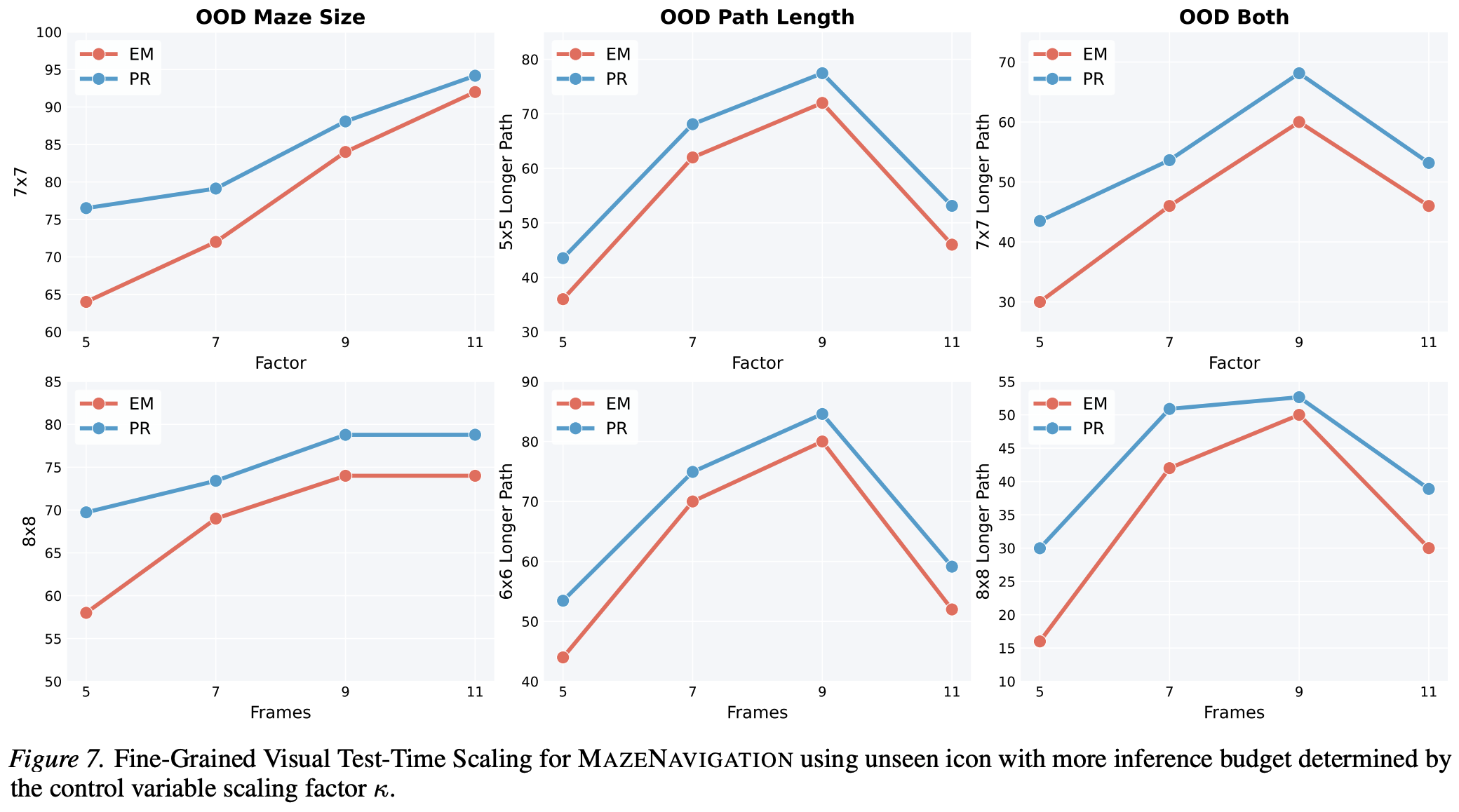
Vision-Language Models have excelled at textual reasoning, but they often struggle with finegrained spatial understanding and continuous action planning, failing to simulate the dynamics required for complex visual reasoning. In this work, we formulate visual reasoning by means of video generation models, positing that generated frames can act as intermediate reasoning steps between initial states and solutions. We evaluate their capacity in two distinct regimes: Maze Navigation for sequential discrete planning with low visual change and Tangram Puzzle for continuous manipulation with high visual change. Our experiments reveal three critical insights: (1) Robust Zero-Shot Generalization: In both tasks, the model demonstrates strong performance on unseen data distributions without specific finetuning. (2) Visual Context: The model effectively uses visual context as explicit control, such as agent icons and tangram shapes, enabling it to maintain high visual consistency and adapt its planning capability robustly to unseen patterns. (3) Visual Test-Time Scaling: We observe a test-time scaling law in sequential planning; increasing the generated video length (visual inference budget) empowers better zero-shot generalization to spatially and temporally complex paths. These findings suggest that video generation is not merely a media tool, but a scalable, generalizable paradigm for visual reasoning.
Quantitative Results
Maze Navigation Quantitative Results
EM = Exact Match, PR = Progress Rate. Proprietary models evaluated zero-shot; open-sourced models fine-tuned. Cyan represents visual reasoning system.
| Model | Input | Output | In Distribution | OOD Maze Sizes | OOD Path Length | OOD Both | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3x3 -- 6x6 | 7x7 | 8x8 | 5x5 (Long) | 6x6 (Long) | 7x7 (Long) | 8x8 (Long) | ||||||||||
| EM | PR | EM | PR | EM | PR | EM | PR | EM | PR | EM | PR | EM | PR | |||
| Proprietary Models | ||||||||||||||||
| GPT-5.1 | 📖+🖼️ | 📖 | 10.6 | 10.7 | 6.32 | 6.72 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| GPT-5.2 | 📖+🖼️ | 📖 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 8.40 | 8.40 | 8.40 | 8.40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Open-Sourced Models (All Fine-Tuned) | ||||||||||||||||
| Qwen3-VL-8B | 📖+🖼️ | 📖 | 58.3 | 68.6 | 20.0 | 37.3 | 19.2 | 34.3 | 0 | 13.3 | 0 | 13.2 | 0 | 11.3 | 0 | 8.9 |
| - w coordinates | 72.0 | 77.3 | 33.2 | 45.0 | 22.0 | 30.5 | 0 | 17.1 | 0 | 13.4 | 0 | 8.1 | 0 | 5.9 | ||
| VPRL-7B * | 🖼️ | 🖼️ | 73.5 | 78.6 | 14.0 | 25.2 | 4.00 | 6.20 | 0 | 11.0 | 2.00 | 16.7 | 0 | 4.10 | 0 | 0.70 |
| Wan2.2-TI2V-5B | 📖+🖼️ | 🎞️ | 96.0 | 99.0 | 90.0 | 92.3 | 80.0 | 83.6 | 44.0 | 55.2 | 42.0 | 51.6 | 40.0 | 51.1 | 32.0 | 47.1 |
| - Unseen Visual Icons | 95.5 | 98.2 | 92.0 | 92.6 | 78.0 | 81.6 | 36.0 | 46.3 | 42.0 | 52.0 | 38.0 | 47.9 | 32.0 | 42.3 | ||
Tangram Quantitative Results
GC. = Goal Completion, BA. = Boundary Adherence. Models are tested on seen puzzle patterns during training for learnability, and unseen patterns for generalizability.
| Model | Input | Output | Seen (Learnability) | Unseen (Generalizability) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strict GC | Progress GC | BA | Strict GC | Progress GC | BA | |||
| Fade-In | ||||||||
| Qwen-Image-Edit-20B | 📖+🖼️ | 🖼️ | 31.0 | 82.3 | 99.8 | 32.0 | 81.3 | 99.7 |
| Wan2.2-TI2V-5B | 📖+🖼️ | 🎞️ | 0.80 | 49.4 | 98.1 | 0.80 | 48.9 | 98.0 |
| Rotation | ||||||||
| Qwen3-VL-8B | 📖+🖼️ | 📖 | 14.4 | 69.7 | 89.5 | 1.6 | 52.1 | 80.8 |
| Nano Banana | 📖+🖼️ | 🖼️ | - | - | - | 9.80 | 43.4 | 64.7 |
| Qwen-Image-Edit-20B | 📖+🖼️ | 🖼️ | 45.2 | 87.5 | 99.7 | 43.2 | 85.7 | 99.6 |
| Wan2.2-TI2V-5B | 📖+🖼️ | 🎞️ | 22.4 | 76.8 | 98.1 | 22.4 | 74.5 | 98.0 |
| Translation | ||||||||
| Qwen3-VL-8B | 📖+🖼️ | 📖 | 28.0 | 75.7 | 91.4 | 1.60 | 58.9 | 82.4 |
| Nano Banana | 📖+🖼️ | 🖼️ | - | - | - | 3.90 | 51.3 | 74.5 |
| Qwen-Image-Edit-20B | 📖+🖼️ | 🖼️ | 85.7 | 97.7 | 99.9 | 76.0 | 95.4 | 99.7 |
| Wan2.2-TI2V-5B | 📖+🖼️ | 🎞️ | 68.0 | 94.7 | 97.0 | 60.8 | 92.0 | 97.0 |
More Qualitative Examples
BibTeX
@article{li2026thinkingframes,
title={Thinking in Frames: How Visual Context and Test-Time Scaling Empower Video Reasoning},
author={Chengzu Li and Zanyi Wang and Jiaang Li and Yi Xu and Han Zhou and Huanyu Zhang and Ruichuan An and Dengyang Jiang and Zhaochong An and Ivan Vulić and Serge Belongie and Anna Korhonen},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2601.21037},
year={2026}
}